Uti Brochure
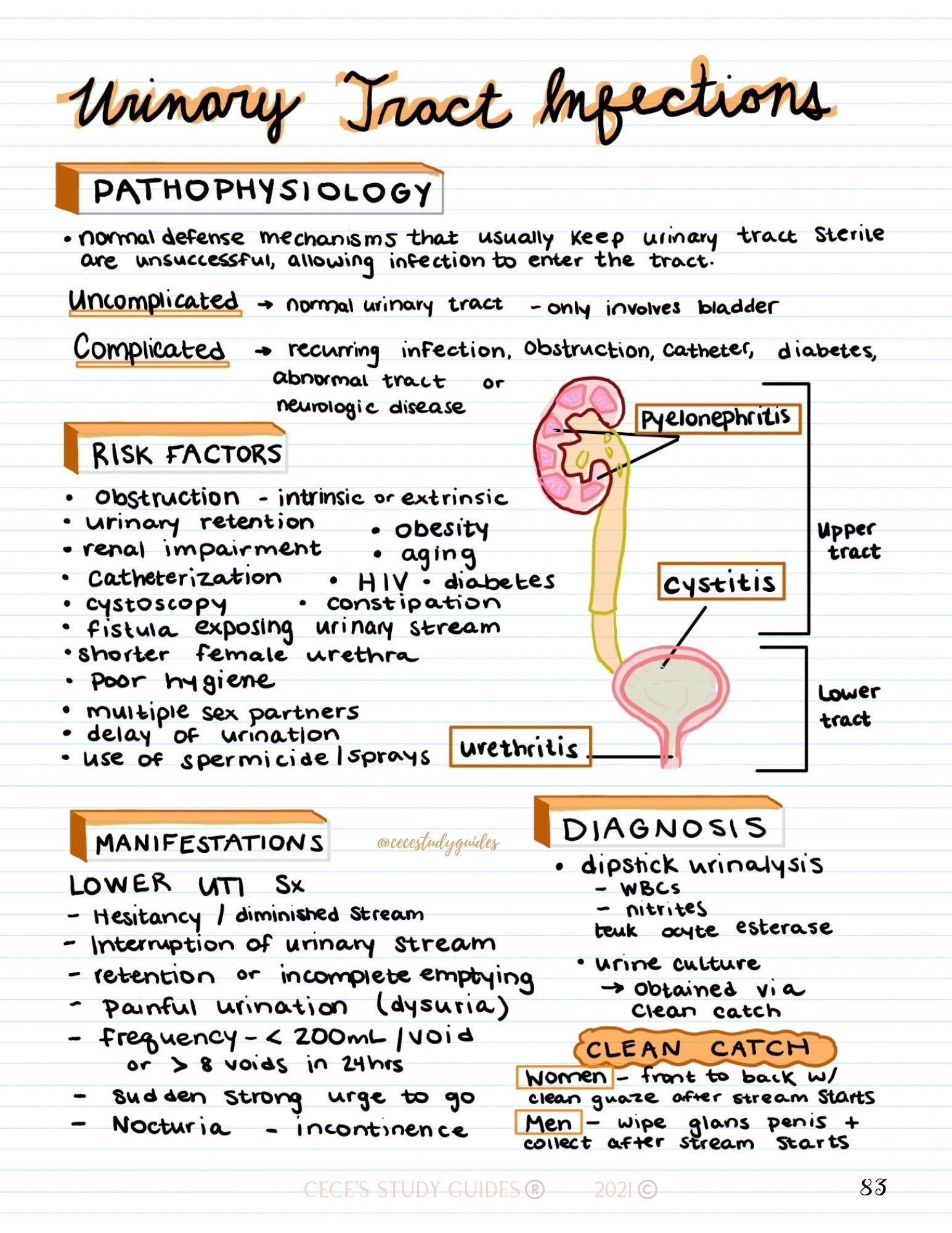
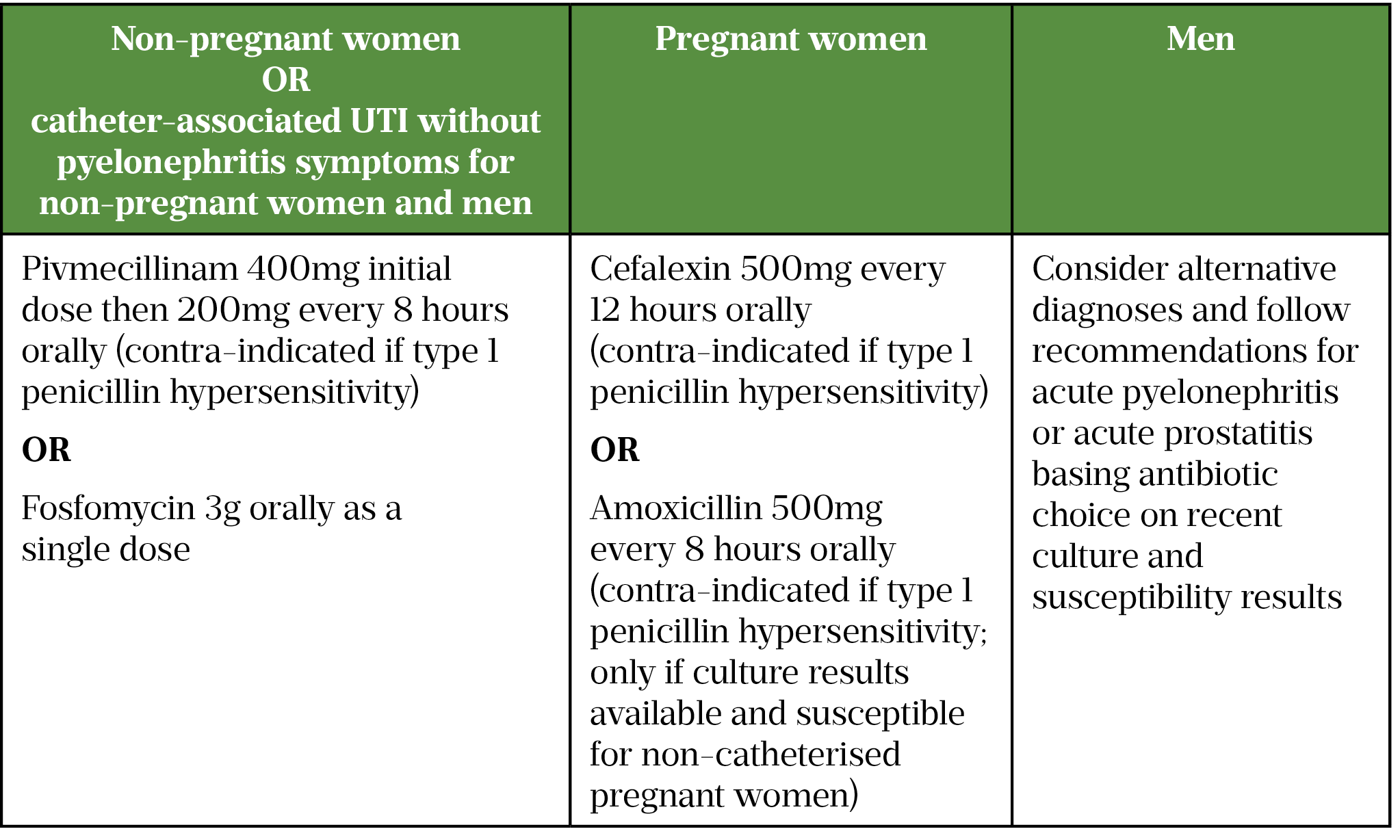
Uti Brochure - • pain or burning when you go to the bathroom. Kidneys, ureters (tubes from the kidneys to bladder), bladder, or urethra (tube. They are typically easy to identify and treat. This includes any part of the urinary tract: This acog patient education pamphlet explains the causes, symptoms, and treatment of urinary tract infections. What is a urinary tract infection? A urinary tract infection (uti) is a bacterial infection in any part of the urinary system — the kidneys, ureters, bladder or urethra. A urinary tract infection (uti) is a bacterial infection in any part of the urinary system — the kidneys, ureters, bladder or urethra. Urethritis is commonly caused by the sexually. Utis are the second most common type of infection in the body and are the reason for more. Infections may occur in different parts of the urinary tract: A urinary tract infection (uti) is a bacterial infection in any part of the urinary system — the kidneys, ureters, bladder or urethra. A urinary tract infection (uti) is a bacterial infection in any part of the urinary system — the kidneys, ureters, bladder or urethra. They are typically easy to identify and treat. Utis are caused by bacteria getting into your urethra or bladder, usually from your gut. Urethritis is commonly caused by the sexually. This acog patient education pamphlet explains the causes, symptoms, and treatment of urinary tract infections. A bladder infection is the. It occurs when bacteria contaminates the urethral opening (the tube that. Bacteria that live in the vagina, genital and anal areas may enter the urethra, travel to the bladder, and cause cystitis. Urinary tract infections (utis) are so common that most people assigned female at birth (afab) will have one at some point in their life. A urinary tract infection (uti) is a bacterial infection in any part of the urinary system — the kidneys, ureters, bladder or urethra. What is a urinary tract infection? Most utis are not serious, but some. Young children have a greater risk of kidney damage linked to utis than older children or adults. Utis affect 3% of children every year. Urinary tract infections (uti) practice points 1) when to suspect a uti only check for a uti if the resident has either: Bacteria that live in the vagina, genital and anal areas may enter the urethra,. This acog patient education pamphlet explains the causes, symptoms, and treatment of urinary tract infections. Kidneys, ureters (tubes from the kidneys to bladder), bladder, or urethra (tube. Infections may occur in different parts of the urinary tract: It occurs when bacteria contaminates the urethral opening (the tube that. Infection in the lower urinary tract. A urinary tract infection (uti) is a bacterial infection in any part of the urinary system — the kidneys, ureters, bladder or urethra. Bacteria that live in the vagina, genital and anal areas may enter the urethra, travel to the bladder, and cause cystitis. Infection in the lower urinary tract. Infections may occur in different parts of the urinary tract:. A urinary tract infection (uti) is a bacterial infection in any part of the urinary system — the kidneys, ureters, bladder or urethra. What is urinary tract infection? Explore challenges of utiimpact of amr on utisbacteria & resistance They are typically easy to identify and treat. What is a urinary tract infection? Bladder infections are more common than kidney infections. It occurs when bacteria contaminates the urethral opening (the tube that. A urinary tract infection (uti) is an infection that can occur anywhere along the urinary tract. They are typically easy to identify and treat. What are the symptoms of a uti? Bacteria that live in the vagina, genital and anal areas may enter the urethra, travel to the bladder, and cause cystitis. Utis are caused by bacteria getting into your urethra or bladder, usually from your gut. Bladder infection, also called a urinary tract infection (uti) or cystitis is a bacterial infection of the urinary bladder. • pain or burning when. Urinary tract infections (uti) practice points 1) when to suspect a uti only check for a uti if the resident has either: Pain or burning when you pass urine. A bladder infection is the most common type of infection. Young children have a greater risk of kidney damage linked to utis than older children or adults. Urethritis is commonly caused. Most utis are not serious, but some can lead to serious problems, like kidney infections. Young children have a greater risk of kidney damage linked to utis than older children or adults. Utis are caused by bacteria getting into your urethra or bladder, usually from your gut. Bladder infections are more common than kidney infections. • pain or burning when. What are the symptoms of a uti? Acute onset of dysuria (burning or stinging when passing urine) or 2. The urinary tract system makes and stores urine and carries it out of the body. They are typically easy to identify and treat. Urine that looks cloudy or smells bad. A urinary tract infection (uti) is when bacteria gets into your urine and travels up to your bladder. Pain or burning when you pass urine. A urinary tract infection (uti) is a bacterial infection in any part of the urinary system — the kidneys, ureters, bladder or urethra. What are the symptoms of a uti? A urinary tract infection (uti) is a bacterial infection in any part of the urinary system — the kidneys, ureters, bladder or urethra. Young children have a greater risk of kidney damage linked to utis than older children or adults. Urinary tract infections (uti) practice points 1) when to suspect a uti only check for a uti if the resident has either: • pain or burning when you go to the bathroom. It occurs when bacteria contaminates the urethral opening (the tube that. Urinary tract infections (utis) are the most common bacterial infections. Explore challenges of utiimpact of amr on utisbacteria & resistance Kidneys, ureters (tubes from the kidneys to bladder), bladder, or urethra (tube. — urinary tract infections, also called utis, are infections that affect either the bladder or the kidneys. A urinary tract infection (uti) is a bacterial infection in any part of the urinary system — the kidneys, ureters, bladder or urethra. What is a urinary tract infection? During the first few months of life,.Urinary Tract Infection Overview (signs and symptoms, pathophysiology
Urinary Tract Infections Nursing Study Guide, MedSurg Cheat Sheet
Updated Urinary Tract Infection Guideline Carolina Antimicrobial
(PDF) Urinary tract infections (UTIs); a leaflet for older adults, and
UTI in Men Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Urinary tract infection in adults diagnosis, management and prevention
Uti Brochure Women PDF Urinary Tract Infection Urinary Bladder
Urinary Tract Infection Medix Urgent Care & Family Health Center
Urinary tract infection resource suite Campaign resources RCGP Learning
What Are the Top Tips for UTI Prevention? Advanced Urology Institute
A Urinary Tract Infection (Uti) Occurs When Bacteria Grow In The Urinary Tract.
Bacteria That Live In The Vagina, Genital And Anal Areas May Enter The Urethra, Travel To The Bladder, And Cause Cystitis.
Urethritis Is Commonly Caused By The Sexually.
Acute Onset Of Dysuria (Burning Or Stinging When Passing Urine) Or 2.
Related Post:



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/urinary-tract-infections-overview-3520507-sketch-FINAL-fab0ff5c6aab400ba4200b3417149979-8c169633a8714e798ec22891baf10189.png)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/urinary-tract-infections-prevention-3520513-Final-97d8fcb9b123490c852ad3480b982792.png)

